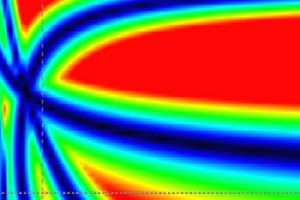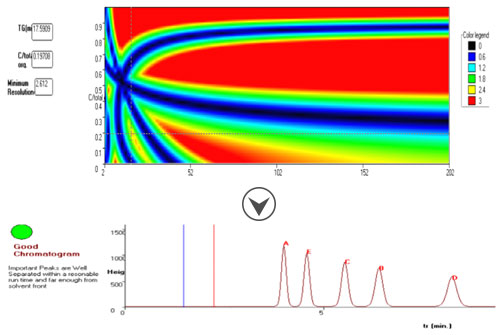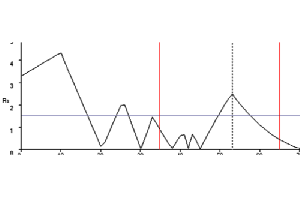
Only two or three initial runs are sufficient to predict all possible separations within one tested parameter.
Basic mode: Optimization of one chromatographic factor
Basic mode: Optimization of one chromatographic factor
Chromocad enables optimization of one factor (such as organic solvent %, pH, temperature,...). Optimization requires only 2-3 initial experimental runs differing in the value of the selected factor for optimization. Chromocad help files provides assisstance in planning the initial experiments. After performing the initial experiments, the retention data are entered into the software interface. This will result into a plot of minimum resolution between peaks as a function of the optmized method parameter. From this plot you can select the optimum condition. Chromocad will predict the chromatogram at the selected condition.
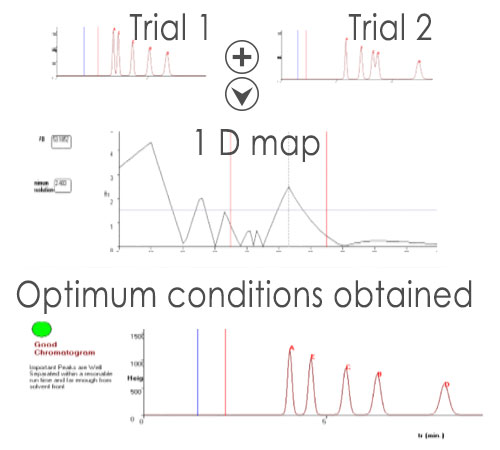
Chromacad supports the optimization of the following chromatographic conditions in 1D mode:
-- Organic solvent % (%B) in Reversed Phase Chromatography.
-- pH of buffer or mobile phase at constant ionic strength- both Henderson-Hazelbach or polynomial models.
-- Temperature.
-- Ion paring agent concentration or amine modifier at constant ionic strength.
-- Buffer concentration in cyano or amino columns.
-- Gradient time.
-- Ternary solvent ratio (ratio of the third organic solvent to the ratio of total organic solvent) .
 Work?
Work? uses the data resulting from few runs performed at different values of one or two method conditions to solve these equations for each compound.
uses the data resulting from few runs performed at different values of one or two method conditions to solve these equations for each compound. apply these solved equations to all proposed values of the studied condition(s) to predict retention times of each compound as well as resolution between peaks.
apply these solved equations to all proposed values of the studied condition(s) to predict retention times of each compound as well as resolution between peaks.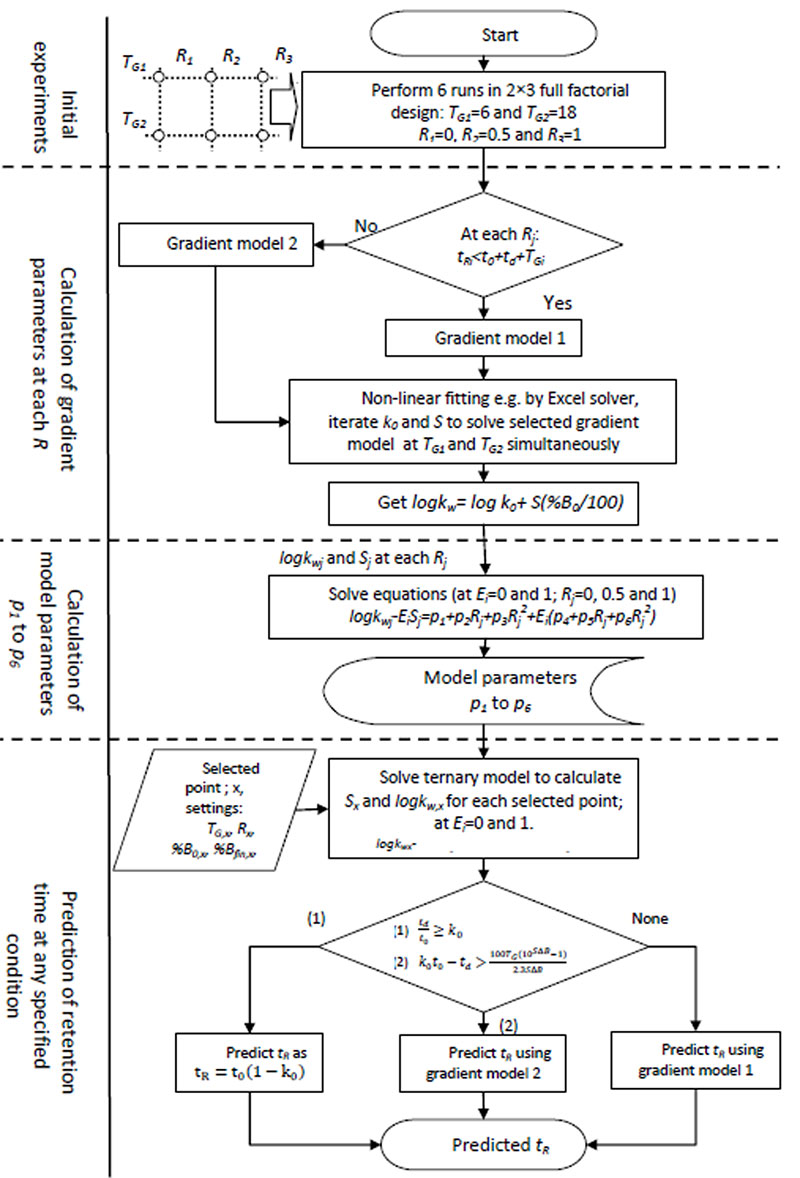
 features
features